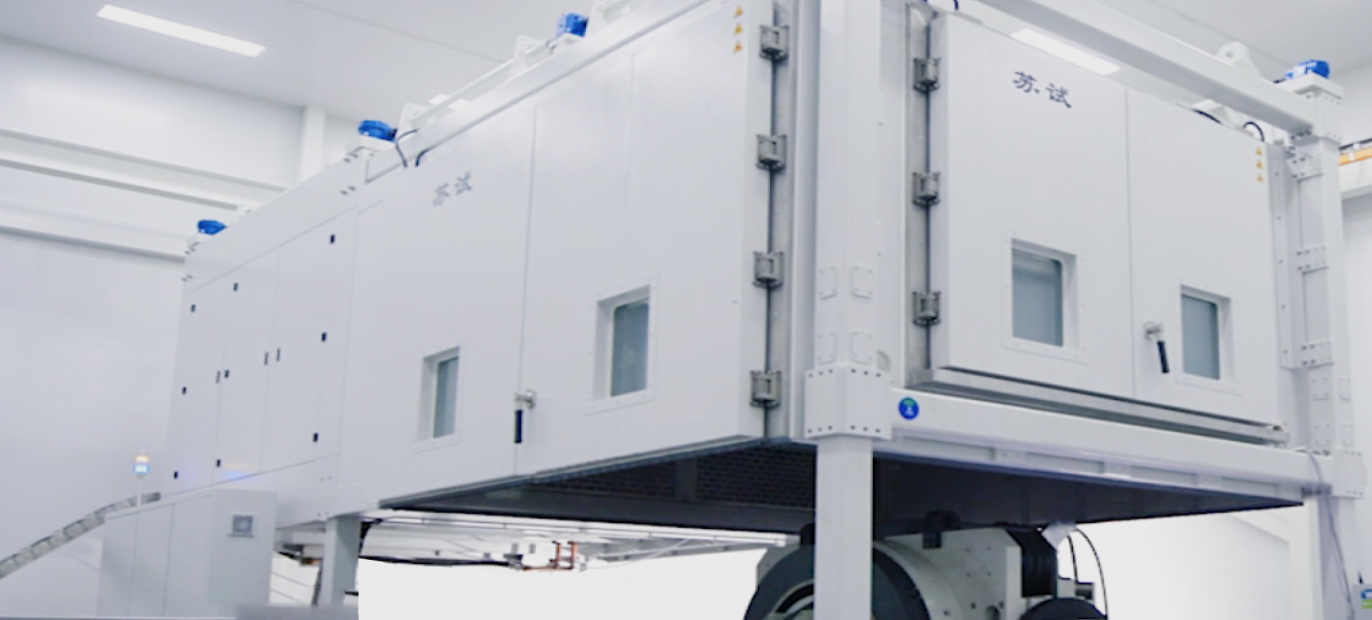
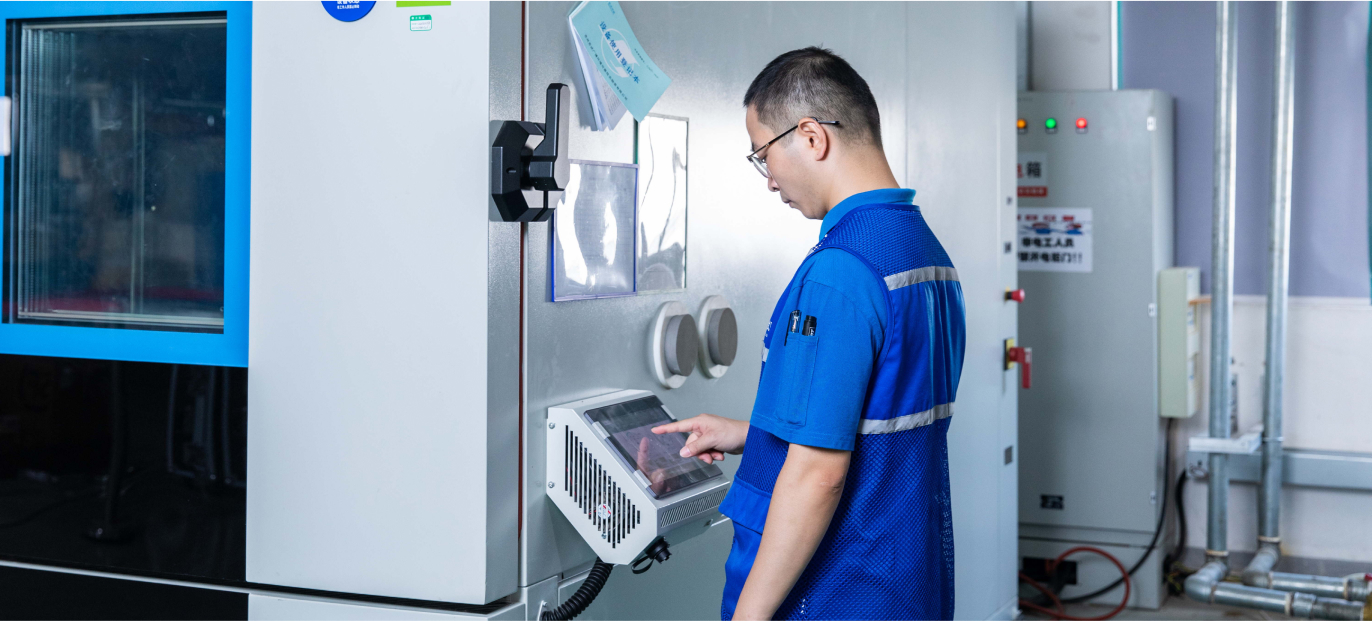
OTA (Over-The-Air) Antenna Performance Testing
(1) Surge in Wireless Communication Devices and Improved Performance Requirements
Driven by the wave of the Internet of Everything, electronic and electrical devices are increasingly equipped with wireless communication functions. From smartphones and tablets to smart home devices and industrial IoT equipment, massive products rely on wireless links for data interaction and remote control. OTA (Over-the-Air) technology, as a convenient means for wireless upgrades and data transmission, has become more popular. As the "antenna" for signal transmission and reception, the performance of antennas directly affects communication quality. For example, in densely populated urban areas, numerous Wi-Fi devices and mobile phones operate simultaneously, causing severe signal interference. If the antenna gain is insufficient or the directivity is poor, devices will frequently lose connection or experience slow internet speeds. In industrial scenarios, poor performance of antennas in wireless sensors on automated production lines will lead to delayed or erroneous data collection, affecting production process control.
(2) Regulatory and Industry Standards Driving Optimization
Regulatory agencies and industry organizations worldwide have introduced a series of regulations and standards to ensure smooth communication and electromagnetic compatibility, putting forward strict requirements for OTA antenna performance in electronic and electrical products. EU CE certification and US FCC certification not only limit the electromagnetic radiation compliance of devices but also involve key indicators such as antenna radiation efficiency and receiving sensitivity. In the communication industry, standards organizations like 3GPP continue to refine antenna performance guidelines for 5G and future communication systems, urging enterprises to optimize product antennas through professional testing to ensure compliance with market access conditions and align with industry development trends.
(1) Mobile Terminal Devices
Including smartphones, tablets, smartwatches, CPE, MIFI, routers, etc.
(2) Consumer Electronics
Including Bluetooth speakers, laptops, smart bracelets, wireless doorbells, etc.
(3) Wireless Communication Modules
Including Wi-Fi modules, Bluetooth modules, ZigBee modules, NB-IoT modules, etc.
(4) Internet of Things (IoT) Devices
Such as smart home appliances, industrial sensors, environmental monitoring equipment, smart logistics tags, etc.
(5) Automotive Electronic Systems
Including in-vehicle entertainment systems, vehicle networking modules, car remote keys, etc.
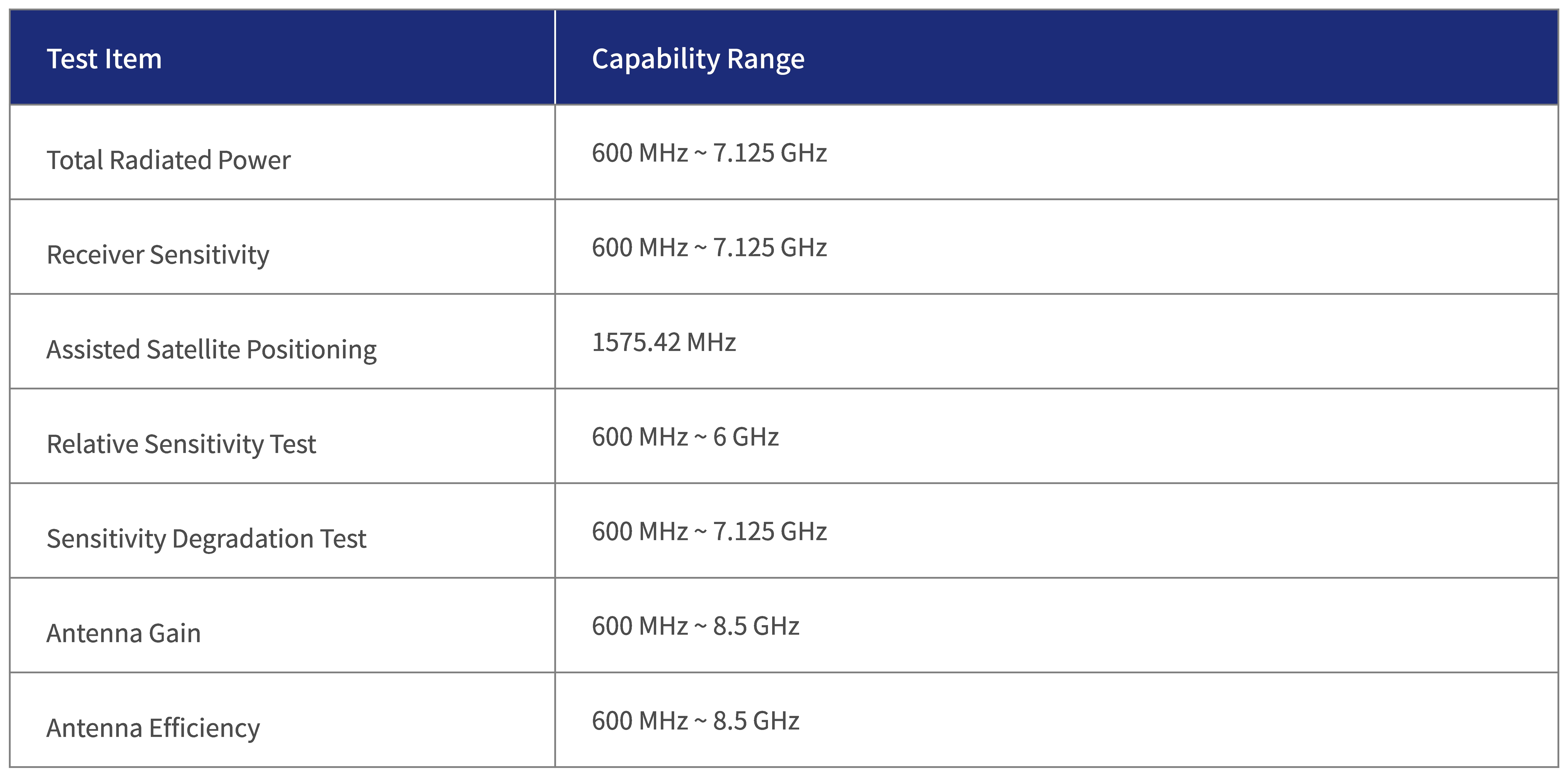
CTIA Certification Test Plan for Wireless Device Over-the-Air Performance
CTIA Certification /Wi-Fi Alliance Test Plan for RF Performance Evaluation of Wi-Fi Mobile Converged Devices
ETSI EN 301 908-2 Chapter 4.2.14, 4.2.15, 5.3.13, 5.3.14
ETSI EN 301 908-13 Chapter 4.2.13, 4.2.14, 5.3.12, 5.3.13
CNAS (China National Accreditation Service for Conformity Assessment)
A2LA (American Association for Laboratory Accreditation)
Nationwide