Electrical Abuse
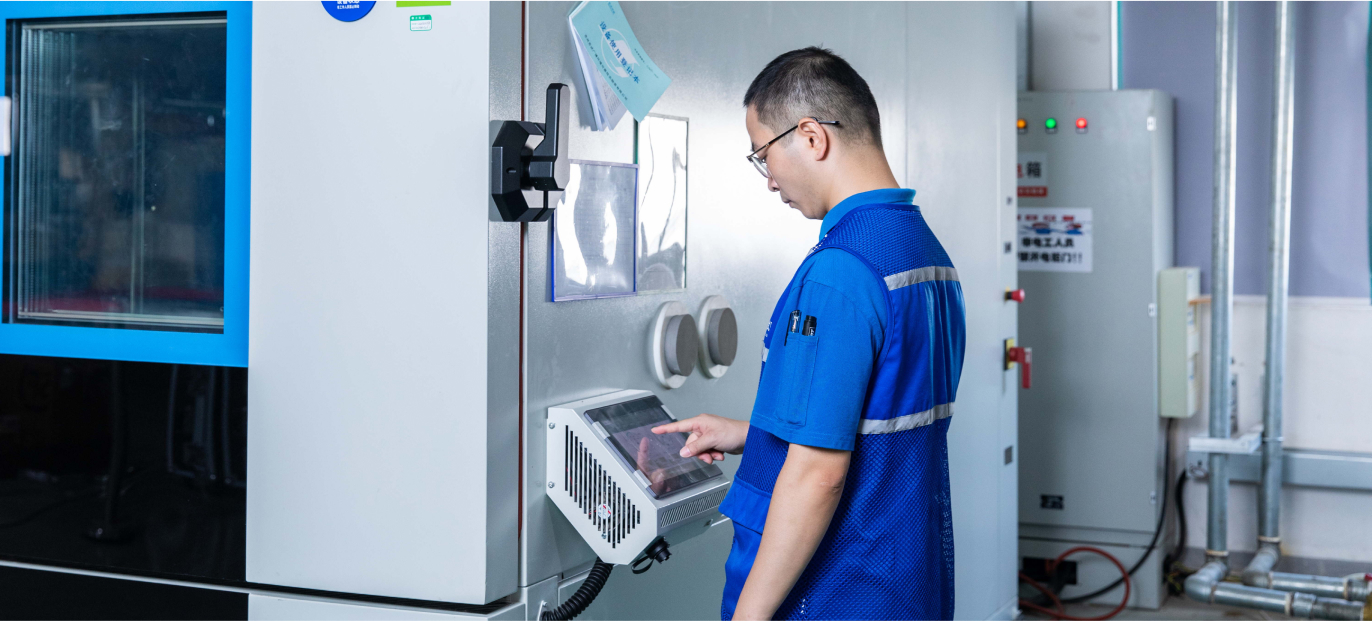
Batteries are intentionally overcharged, overheated, or damaged to test their reaction to these extreme conditions. The purpose of such tests is to check the behavior of the battery under abuse conditions to ensure it is safe, reliable, and does not pose a hazard. Electrical abuse testing is a destructive safety test for batteries. Destructive testing can minimize the risk of accidents and fires, ensuring higher safety and reliability. They are also a prerequisite for the marketing and development of new types of batteries.
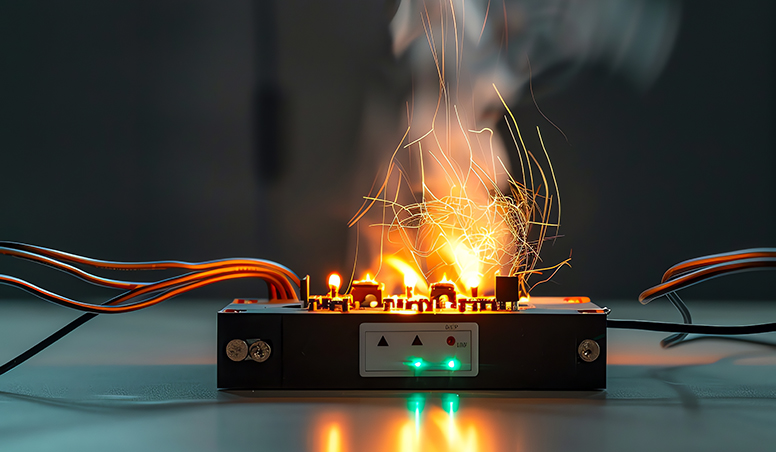
Overcharge, overcharge protection, overcharge performance test, over-discharge, charging after over-discharge, discharging after over-charge, internal short circuit, external short circuit, etc.
Voltage Range: -10 to 1,200V
Discharge Current: 0 to 3,000A
Charge Current: 0 to 1,800A
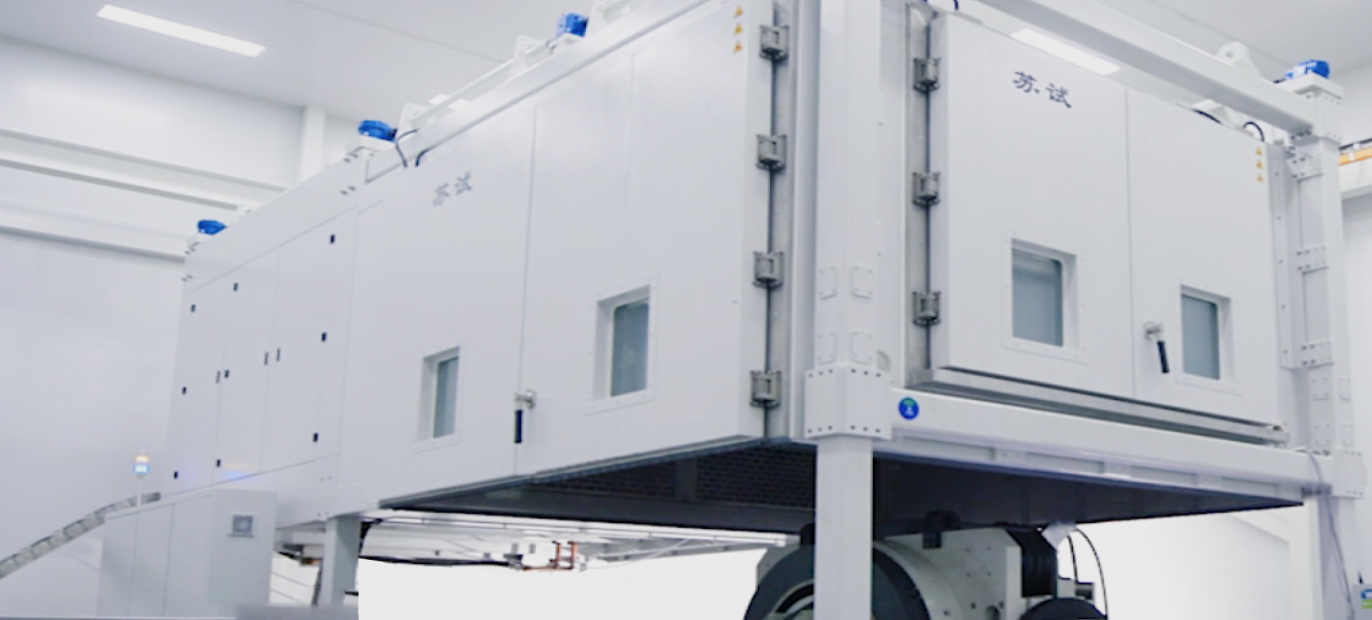
Volume: 806m³, 26m*5m*6.2m (D*W*H), Temperature: -60°C to 80°C
Volume: 24m³, 3.3m*3.3m*2.2m (D*W*H), Temperature: -70°C to 200°C
Temperature Change Rate: ≤5°C/min
ANSI/CAN/UL/ULC 2580, IEC 62281, IEC 62133, IEC 62619, UN38.3(ST/SG/AC.10/11/Rev.7/Amend.1) , etc.